The Challenge:
Low surface energy polymers like silicone elastomers and high-density polyethylene (HDPE) present challenges in achieving strong adhesion with traditional bonding methods due to their hydrophobicity and chemical inertness. The lack of surface reactivity can lead to adhesion failures in applications like bonding or potting. Developing robust adhesion is critical for manufacturing products with integrated polymer components.
The (Experimental) Process:
To find a solution, SES Force-4 studied two common low surface energy polymers: silicone elastomer and high-density polyethylene (HDPE). The study employed compressed air plasma treatment as a reliable method to enhance adhesion on low surface energy polymers. Both polymers were exposed to compressed air plasma treatment in a vacuum chamber for 2 minutes. This surface modification technique aimed to improve the adhesion strength of materials that typically do not bond well without surface modification.
Results:
After exposure to plasma treatment, both silicone and HDPE substrates showed enhancements in wettability. Silicone was completely wettable with a 0 degree contact angle. HDPE exhibited a contact angle between 28-35 degrees.
Silicone Elastomer:
Hydrophobic recovery occurred within a few hours after compressed air plasma treatment, as measured by contact angles. Even after three days, the silicone elastomer surface remained receptive to a medical-grade epoxy, demonstrating a prolonged enhancement in adhesion.
HDPE Plastic:
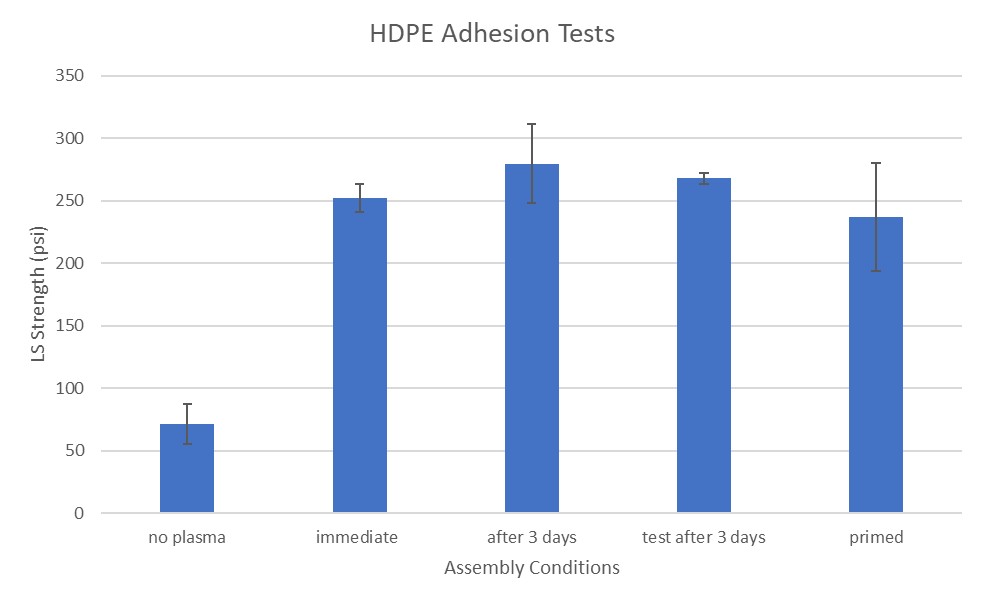
Hydrophobic recovery on HDPE was slower than silicone elastomer, but the adhesion enhancement persisted for days after assembly.
Adhesion Tests:
Adhesion tests on plasma-treated surfaces resulted in substrate failure, indicating strong bonding between the treated surface and the adhesive. Non-plasma-treated surfaces showed adhesion failure, underscoring the necessity of surface modification for effective bonding.
Hydrophobic Recovery:
The study found that water contact angle measurements alone might not be the most reliable indicator of epoxy wettability, considering the hydrophobic recovery observed on silicone elastomer.
![]()
The Conclusion:
The study highlights the importance of well-designed adhesion tests on surfaces of interest to accurately assess and predict adhesion performance.
It is imperative to understand interfaces when selecting adhesives for bonding or potting applications, especially when dealing with low surface energy polymers. While compressed air plasma treatment proved effective in enhancing adhesion, the study revealed that water contact angles might not fully capture the complexities of surface interactions. Well-designed adhesion tests on treated surfaces emerged as the most reliable approach to prevent adhesion failures in subsequent stages of the product development cycle. This knowledge contributes to more informed decisions in material selection and adhesive application, ultimately improving the reliability and durability of bonded products.
Author
Aniruddha (Andy) Palsule, PhD. – Polymer Scientist

Keep in touch with us.
Sign up for our newsletter.